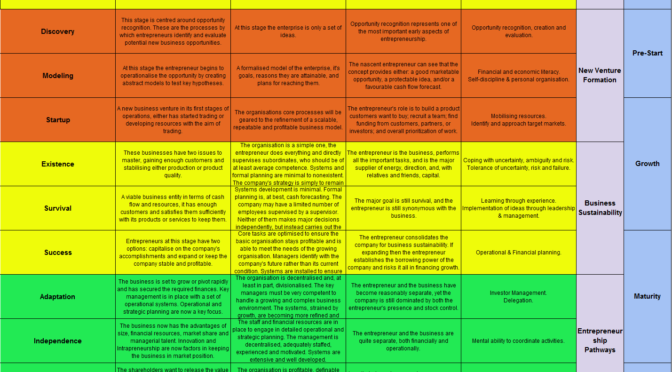
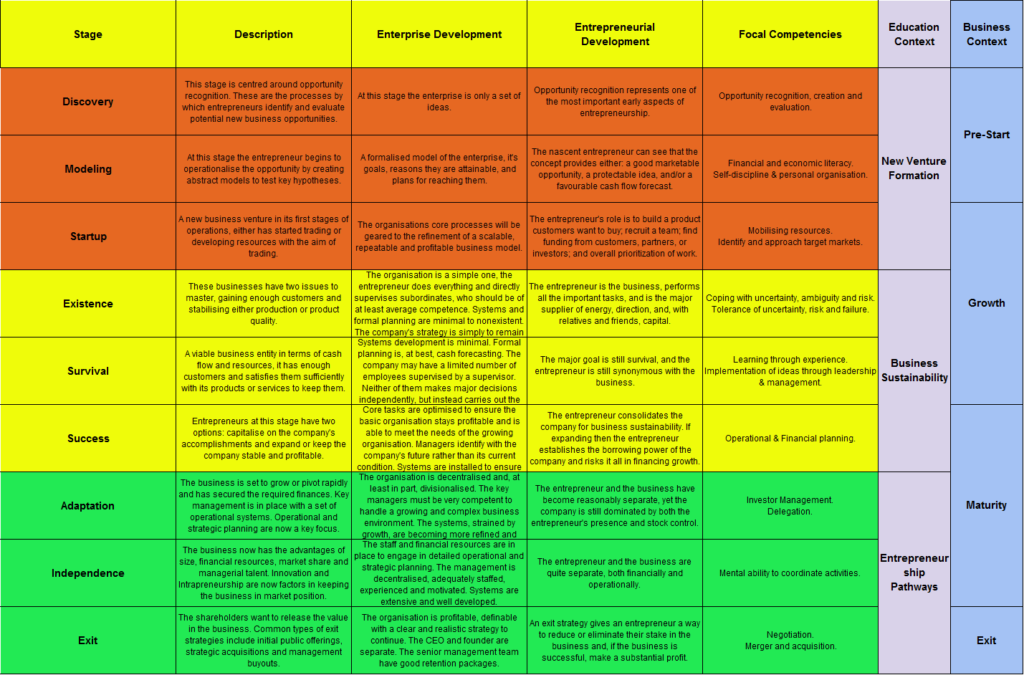
The productivity of a business is controlled by a number of factors and as entrepreneurs we need to understand these factors to ensure we have sustainable businesses. So what do we mean by productivity?
Productivity is very simply defined as the ratio between output and input. Therefore increasing productivity means greater efficiency in producing output of goods and services from labour, capital, materials and any other necessary inputs.
It’s more important metric than just measuring this ratio, as it provides a benchmark by which you can measure nations, regions, industries and and most importantly for us entrepreneurs, businesses. Businesses which have higher productivity are more sustainable and therefore employees have safer jobs, paying more taxes and enable stable economic structures surrounding these businesses.
So when I review the literature on productivity I have found a number of factors which control productivity, we can put these down to eight controlling factors, In alphabetical order:
- Finance
- Industry & Market
- International Trade
- Management
- People
- Place
- Processes
- Technology
Finance
The financial capital structure of a business dictates the productivity of the business. Managers are instructed to maximize shareholders benefits and if this requires short-term (annual) rewards then this may not beneficial for the longer term productivity aims. Hill, C. W., & Snell, S. A. (1989) found that businesses with one or more of the following; a diversification strategy, R&D expenditure, capital intensity and stock concentration were all important financial factors in a business productivity. At a national level Guariglia, A., & Santos-Paulino, A. U. (2008) found that national GDP per capita and national investment generally exert a positive and significant effect on business productivity.
Industry & Market
The level of productivity is related to the industry as some industries are highly automated whilst others are still manual handmade. It’s also dictated by the market, some customers require personalised service while others want fully online and automated. One example is holidays, some people want book online without ever talking to a person from that company whilst others require a home visit and discussion of every aspect of the holiday.
The OECD provides a detailed list of productivity data sets whilst the UK provides this, and many other countries do the same.
International Trade
Trade increases productivity. Badinger, H., & Breuss, F. (2008) found an increase in the export ratio of a manufacturing business by one percentage point increases productivity by 0.6 percent on average. To be able to export your products or services a business should be of a comparable price and quality and therefore productivity. Export focused businesses have therefore higher productivity Guariglia, A., & Santos-Paulino, A. U. (2008).
Management
A number of these factors requires good management and leadership. However, a considerable amount of research has consistently found that use of effective human resource management practices enhances firm performance. Specifically, extensive recruitment, selection, and training procedures; formal information sharing, attitude assessment, job design, grievance procedures, and labour-management participation programs; and performance appraisal, promotion, and incentive compensation systems that recognize and reward employee merit have all been widely linked with valued firm-level outcomes. Huselid, M. A. (1995) and others have argued that the use of these practices will result in greater business performance, independent of the industry and business size.
People
Bakker (2014) demonstrated that to ensure a knowledge worker is optimally productive and happy, it is important that he or she can attain personal objectives and that facilities and services fit with personal needs. Bailey (1993) noted that the contribution of even a highly skilled and motivated workforce will be limited if jobs are structured, or programmed, in such a way that employees, who presumably know their work better than anyone else, do not have the opportunity to use their skillset. Most academic frameworks present variables including buildings and facilities, work processes, organisational characteristics, personal characteristics and the external context may have an impact on labour productivity (Clements-Croome, 2000; Van der Voordt, 2003; Batenburg and Van der Voordt, 2008; Mawson, 2002; Haynes, 2007).
Place
Especially within the service industry, location is one of the most important factors. The best coffee in the world may be served in Seattle but living in Cirencester doesn’t allow me to get my daily fix from there. However, the competitive environment in these two places will be different and therefore I would guess the productivity of a coffee shop in Seattle will have to be higher than that in Cirencester. (Due to taxes, real estate costs, staffing, ..etc)
We should also take into consideration business clusters, which also draws in the people and process factors. Business which form clusters will end up employing the same staff over time and therefore develop similar processes. Clusters are concentrations of highly specialized skills and knowledge, institutions, rivals, related businesses, and sophisticated customers in a particular nation or region. Proximity in geographic, cultural, and institutional terms allows special access, special relationships, better information, powerful incentives, and other advantages in productivity and productivity growth that are difficult to tap from a distance. As a result, in a cluster, the whole is greater than the sum of the parts.
Each location has a unique set of taxes, international trade arrangements and laws which dictate the level of productivity. Some industries are protected by law and therefore can operate with lower or higher productivity.
Processes
The first set of innovation around productivity was designing processes to improve productivity by simplifying the task, for example Ford’s production line and McDonald’s restaurant. Process engineering focuses on the design, operation, control, optimization and intensification of processes. In a knowledge economy this is typically information and data through electronic means. Data like money is not worth anything if it is not used or traded, also like money needs to be kept secure and have some form of traceability.
Technology
In traditional manufacturing (Think car manufacturing) the first stage of increasing productivity was designing the processes so that a person could do a smaller task faster, then using a machine to semi-automate the task and finally reducing the role of the person down to supervision and maintenance.
The computer has increased the productivity of many increases, most notable the Banking which now allow us access to our money from our phones, no longer having to go to a branch. Service industry productivity is increasing faster than manufacturing over the last twenty years.
For the knowledge and service economy this requires typically a computer to have knowledge and provide service. So if we are booking a flight, then the computer needs to have been programmed with a process to book one or more flights and a complete list of flights and there availability. The problem arises when you say I want to fly anywhere on friday night. So in these industries AI will provide the increased productivity that robots have provided in the car manufacturing industry.












 Born: 25th November, 1835
Born: 25th November, 1835 Born: 23 October 1942
Born: 23 October 1942