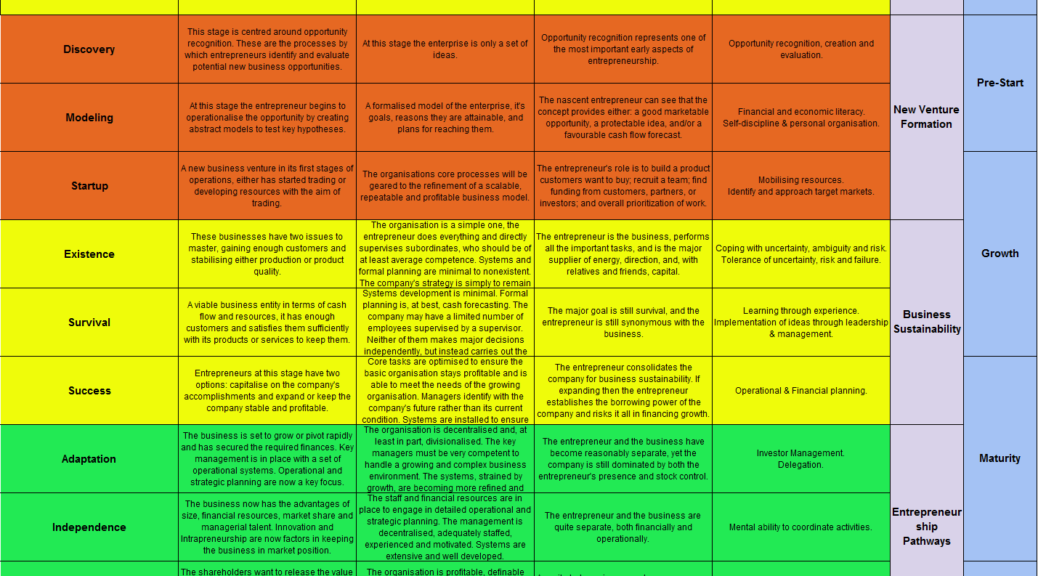
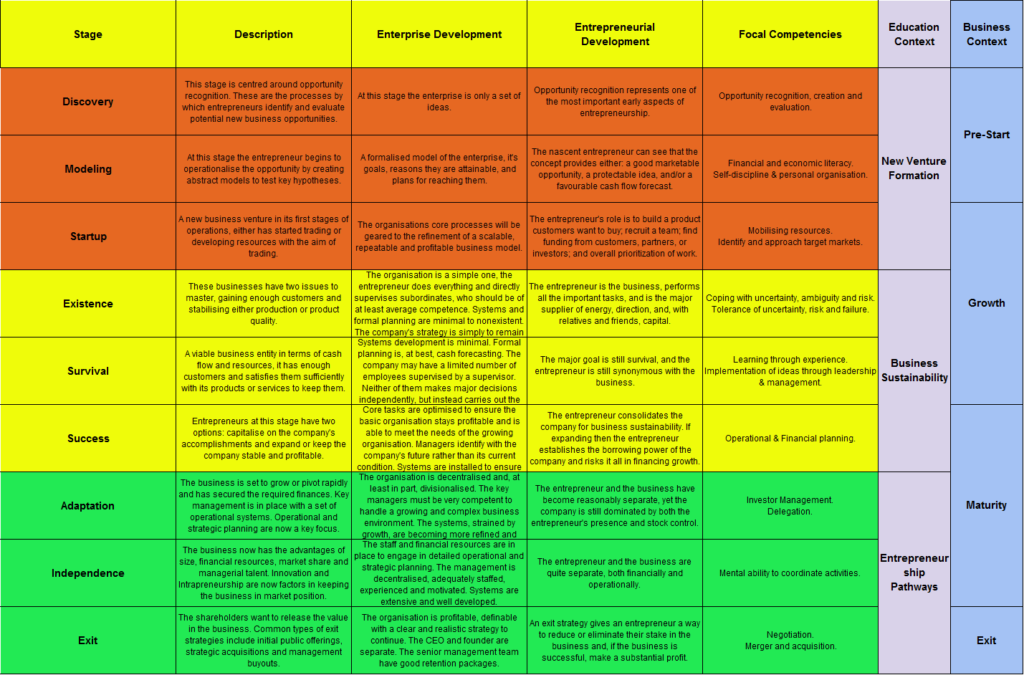
Summary
The rise of entrepreneurship education in the United States has played a significant role in shaping the country’s economic landscape. This paper explores the impact of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial behavior and research, highlighting its contributions to fostering innovation, economic growth, and job creation. By analyzing current literature, policy developments, and case studies, this paper establishes the importance of entrepreneurship education in driving the entrepreneurial spirit in the United States.
Introduction
Entrepreneurship education in the United States has grown exponentially over the past few decades. This growth has played a pivotal role in fostering innovation and economic growth, as well as promoting job creation in the country. This paper aims to delve into the impact of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial behavior and research in the United States, focusing on its role in driving the entrepreneurial spirit and creating a more prosperous economy.
The Importance of Entrepreneurship Education
Entrepreneurship education is a vital component of economic growth and innovation. According to Kuratko (2005), “entrepreneurship education can serve as a catalyst for economic growth and revitalization, as it equips individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to create, manage, and grow new business ventures” (p. 578). Entrepreneurship education programs provide students with a wide range of skills and abilities that go beyond traditional business education, including creativity, innovation, problem-solving, and risk-taking (Solomon, 2007).
The Growth of Entrepreneurship Education in the United States
Entrepreneurship education in the United States has seen significant growth in recent years. According to a study by the Kauffman Foundation (2013), the number of entrepreneurship courses offered at U.S. colleges and universities increased from 250 in 1985 to more than 5,000 in 2013. Furthermore, nearly 90% of American universities now offer courses related to entrepreneurship (Kauffman Foundation, 2013).
This growth in entrepreneurship education can be attributed to a combination of factors, including increased demand for entrepreneurial skills, changing economic conditions, and supportive government policies. As the U.S. economy shifted from manufacturing to knowledge-based industries, the need for innovative and entrepreneurial individuals became more critical (Audretsch & Keilbach, 2007).
Government Support for Entrepreneurship Education
The U.S. government has been instrumental in promoting entrepreneurship education through various policies and initiatives. For instance, the Small Business Administration (SBA) provides resources and support for entrepreneurs, including educational programs, mentoring, and access to capital (SBA, 2021). Additionally, the federal government’s support for research and development (R&D) has helped spur entrepreneurial activity, as evidenced by the success of programs like the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) (Audretsch, 2012).
The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education on Innovation
Entrepreneurship education has played a crucial role in fostering innovation in the United States. By equipping students with the necessary skills and mindset, entrepreneurship education has contributed to the development of groundbreaking products, services, and business models. For example, companies such as Google, Facebook, and Tesla, founded by entrepreneurs who emerged from educational institutions with strong entrepreneurship programs, have revolutionized their respective industries (Solomon, 2007).
The literature suggests that entrepreneurship education has a positive impact on students’ propensity to innovate. According to a study conducted by Peterman and Kennedy (2003), students who participated in entrepreneurship education programs exhibited higher levels of innovative behavior and were more likely to generate novel business ideas. This finding is supported by Lorz, Mueller, and Volery (2013), who found that entrepreneurship education programs increased students