As a entrepreneur, you can have a lifestyle of freedom and flexibility not offered to an employee. However, being a owner of a small business also carries greater responsibility with many more tasks to juggle. This means you need to understand the tasks required by everyone around.
Entrepreneur
- Planning and Strategy – You are the principal strategist and planner.
- Finance and Accounting – Depending on the business, some owners can bootstrap and start with a smaller budget, but either way you’ll also need to set up and maintain business bank accounts, payment processing, accounts payable and accounts receivable, and taxes.
- Legal – From forming a limited liability company to creating legal contracts. You might need to write, review and sign legal contracts and sales agreements.
- Marketing and Sales – No matter how good your product or service is, you need marketing and sales to drive business. Depending on the business, you could be doing print advertising, public relations, online marketing, networking, cold calling and managing commissioned salespeople.
- Customer Service – In the beginning, most entrepreneurs are responsible for conducting all of the customer service duties. These include phone calls, email messages and follow-ups concerning product delivery and quality issues.
- Human Resources – As a small business grows, so do its hiring needs to accommodate more orders and faster growth. The entrepreneur needs to identify human resources needs, write job descriptions, screen and interview candidates, train, manage and pay employees.
Customers
Nurturing relationships with your customers is a crucial part of growing a startup business. In this age of ecommerce and technology innovation, caring for your customers has never been more important.
The easiest way to get, keep and get your loyal customer to promote your business is to:
Interact with your customers
Here are some simple lessons:
- Keeping your patience is key to giving your customer the time to air out their issue.
- Do everything in your power to provide excellent service to your customers on an ongoing basis.
- it’s important to truly listen
- Treat a Customer Like a Valued Partner
- Build Trust by alerting your customers to Large Scale Changes, Good or Bad
- Being transparent in the digital age is a must.
- No matter the circumstance, the customer is always right.
Business operations
This is the core of the business, it handles everything. If you can understand what this does and how it does it, to provide an excellent customer experience each time within budget, your business has the best opportunity for success. Don’t leave any stone unturned in making your operation understandable by ALL stakeholders in the business, staff, shareholders and most importantly your customers.
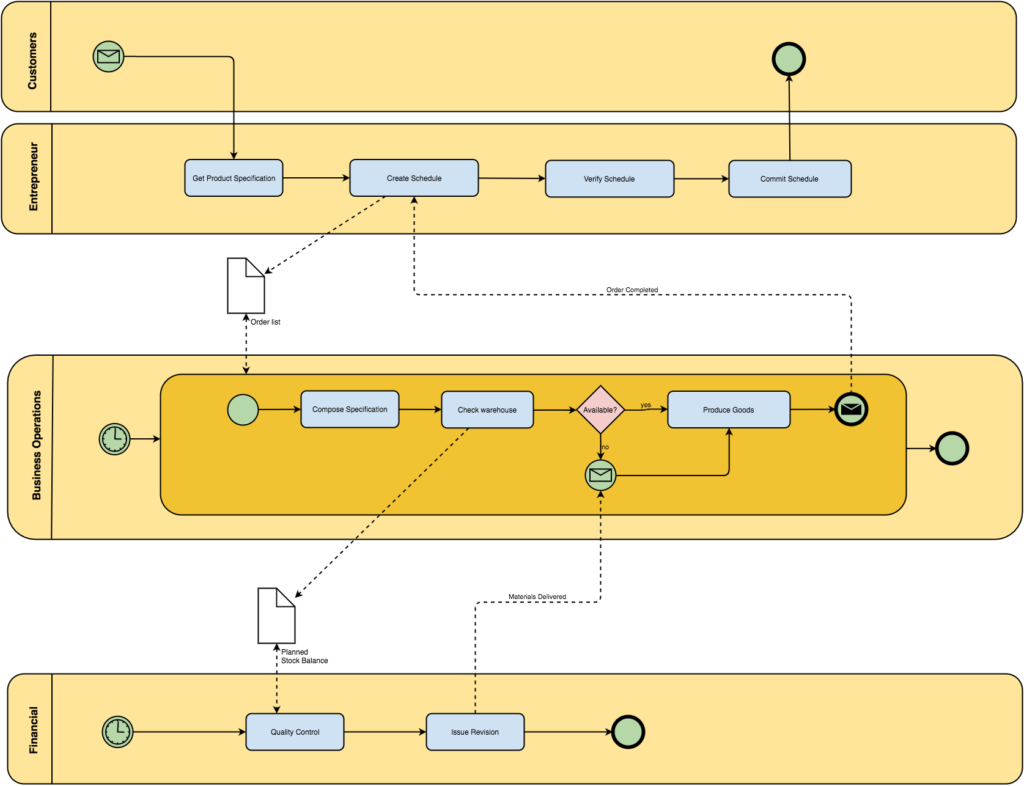
Financial
Financial planning and cash management is fundamental to a startup. Perhaps the most challenging part of building a startup is forecasting revenue targets. You can take one of two approaches; a top down and bottom up approach.
- The top down approach involves identifying comparable companies to yours that have grown to be successful and modeling your revenue growth curve similar to these companies.
- The bottom up approach makes use of your market research to look at how many customers you can reach, the number you can persuade to work with you and how many you can capture as paying customers.
The final step in your financial plan is to develop your cash flows. Revenue minus cost of goods provides positive cash and operating expenses and capital expenses (purchase of assets) use up cash. Every startup must have a good view on how much cash they will need to get through each phase of the business.